We analyzed refrigerator energy usage data from the U.S. Dept. of Energy and ENERGY STAR® for 3,279 residential refrigerators and refrigerator/freezers to find the average annual, daily, and hourly wattage they use and then categorized the results by refrigerator type, features, and size.
Key Findings About Refrigerator Electricity Consumption
- How much power a refrigerator uses varies greatly by the type of refrigerator, its size and features, age, frequency of use, and the environment where it is located.
- Knowing your refrigerator’s running and starting watts (surge watts) will help you pick the right size portable power station or generator to keep your fridge running in the event of a power outage.
- On average, data showed a single-door refrigerator, the type without a freezer, uses 804 watts per day (34 watts per hour).
- On average, data showed that refrigerators with freezers (all types) use 1,429 watts per day (60 watts per hour).
- Common residential refrigerators can use between 350 and 1,200 starting watts, depending on the refrigerator’s compressor size, efficiency, and age.
Table of Contents
Related Articles
How Many Watts Does a Refrigerator Use?
The average refrigerator freezer uses 1,429 watts / day. Or, about 60 watts per hour to run.
Appliance power consumption often varies by the size, age, features, frequency of use and surrounding environment and refrigerators are no exception.
Below is a table summarizing average fridge power consumption across all sizes and features. A more detailed Refrigerator Wattage Chart is further down the page.
Average Refrigerator Power Consumption by Type & Size
| Refrigerator Type | Average Size (cubic feet) | Average Annual Energy Use (kWh/yr) | Average Watt Hours Used / Day (Wh/day) | Average Watts Used / Hour (W/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator w/ Freezer - All | 20 | 522 | 1429 | 60 |
| Bottom Freezer | 20 | 547 | 1499 | 62 |
| Side-by-Side | 24 | 657 | 1800 | 75 |
| Top Freezer | 16 | 361 | 989 | 41 |
| Refrigerator w/o Freezer | 16 | 293 | 804 | 34 |
How to Find a Refrigerator’s Wattage
Your refrigerator should come with an energy rating that will include an estimate of its yearly energy use. In the U.S., this is called an ENERGY STAR® rating.
ENERGY STAR® provides the estimated yearly electricity use information for refrigerators, freezers, mini fridges, and other household appliances.
With the Estimated Yearly Electricity Use rating from the ENERGY STAR® label, we can do some easy math to find the average daily and hourly watt usage of your refrigerator model.
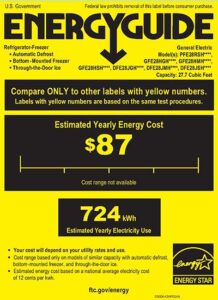
Example: How to Calculate a Refrigerator’s Daily & Hourly Average Wattage
My 27.7 cubic ft. GE refrigerator’s estimated yearly electricity use is 724 kWh, so let’s use that data and find my refrigerator’s daily and hourly power consumption.
- Multiple kWh by 1,000 to get Watts.
724 kWh x 1,000 W/kW = 724,000 Wh - Next, divide watts (W) by 365 days, to get watts per day.
742,000 W / 365 days = 1,984 W/day
This is the average amount of electricity used per day. - Last, divide watts/day (W/day) by 24 hours, to get watts/hour (W/h).
(1,984 W/day) / (24 hours/day) = 82.6 W/hour
This is the average amount of electricity used per hour.
How to Measure a Refrigerator’s Watt Usage
The best way to measure how many watts your refrigerator uses is to plug it into an electricity usage meter. They’re inexpensive and super easy to use.
Just plug your refrigerator into the meter and plug the meter into your wall outlet. You’ll be able to see how many watts, volts, and amps are being used in real-time and track electricity consumption over time.

Example: Measuring Refrigerator Wattage
I plugged my 27.7 cubic ft. GE bottom-freezer refrigerator, Model No. GFE28HSHGSS, manufactured in 2016 into my electricity monitor for 48 hours. At the end of the 48 hours, my fridge used a little over 4 kWh of energy, or about 84 Wh (watt hours) per hour on average.
Side Note: An electricity usage meter is handy to have when you’re trying to choose the right size portable power station, solar generator, or backup generator because you can easily measure the watt usage of the 110-120v plug-in appliances that you want to power.

How Many Starting Watts Does a Refrigerator Use?
Refrigerators require between 350 to 1,200 starting watts. Exactly how much depends on the size and efficiency of the compressor in the refrigerator.
Starting watts are sometimes referred to as surge watts but the technical term is locked rotor amps (LRA or LRa).
Locked rotor amps are the amount of power required to start the moving parts of a motor when it is first turned on. Once the compressor is running under normal operation, which usually takes less than a second or two, the power needed to run the compressor drops below the starting watt requirements.
How to Calculate Refrigerator Starting Watts
To calculate the starting watts of your refrigerator you need to know the required voltage and starting amps of the compressor motor in your refrigerator.
You can find this information on the manufacturer’s label or on the label on the refrigerator’s compressor.
- Open the door(s) to your refrigerator and look for the manufacturer’s label. Depending on the manufacturer, the label may say Rated Current or just list the starting watts in a line of other information.
- (Figure 1) The Samsung label shows the Rated Current, or starting amps, required for this refrigerator to start would be 5.0 A (amps) on a 115V circuit.
- (Figure 2) The label for my older GE refrigerator has the amp requirements on a single line, along with volts and hertz. Figure 2 shows that this model of fridge requires 9.5 amps on a 110 to 127 volt circuit for the compressor to start.


You can also find the starting amps, or locked rotor amps (LRA), on the refrigerator’s compressor.
- This requires removing the back cover of the fridge so it is not the preferred method, but if you can’t find the label in the refrigerated compartment area this may be a workable alternative.
- (Figure 3) The label on the compressor for my GE fridge shows a 9.3 LRA and 115 to 127 volts.

Calculating Starting Watts
To calculate the starting watts of a refrigerator, multiply starting amps by the voltage.
Starting Amps X Volts = Starting WattsFor example, my fridge is plugged into a 120 volt circuit and it takes 9.5 amps to start the compressor and begin to cool down the refrigerator.
9.5 starting amps X 120 volts = 1,140 starting wattsThis means my refrigerator needs at least 1,140 starting watts of power to start the rotor in the compressor motor turning. Once the motor is up to speed the amount of power it needs to keep running will decrease.
Starting watts are typically not an issue if you’re connected to the grid because there is essentially limitless power to draw from.
But that’s not the case if you get disconnected from the grid by a blackout, load shedding, or just want to go off grid altogether.
What Size Portable Power Station to Run a Refrigerator?
There are three factors you will need to be able to determine the right size portable power station to run your refrigerator.
- How many watts your refrigerator uses per hour.
- How long you would like to power your refrigerator.
- How many starting watts your refrigerator requires.
For example, let’s say there’s going to be a 6-hour power outage and I don’t want the food in my refrigerator to spoil. To overcome this, I want a portable power station that can run my fridge for at least 6 hours.
We already know that the average wattage used by my fridge is 84 Wh/hour. Next, we need to know how many watts I need to power my refrigerator for 6 hours.
To find watt hours needed, use the formula:
Watt hours/hour X hours you want to power your appliances = Watt hours neededTo run my refrigerator for 6 hours I’ll need:
84 Wh/hour x 6 hours = 506 WhThe calculation above shows that I need a portable power station that can provide a minimum of 506-watt hours of electricity.
I also need enough starting watt capacity to start my refrigerator’s compressor. My refrigerator requires 1,140 starting watts.
The portable power station I need to run my refrigerator for 6 hours needs to have at least 506 Wh (Watt hours) of power capacity and provide starting watts above 1,140 watts.
Refrigerator Wattage Chart – Average Watts Used by Fridge Type, Features, & Size
| Refrigerator w/ Bottom Freezer By Features & Size | Average Annual Energy Use (kWh/yr) | Average Watt Hours Used / Day (Wh/day) | Average Watts Used / Hour (W/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost, Without: Icemaker (Overall) | 426 | 1,167 | 146 |
| 9 to 14 cubic ft. | 373 | 1,022 | 128 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 444 | 1,216 | 152 |
| 20 to 24.9 cubic ft. | 493 | 1,351 | 169 |
| 25 to 30 cubic ft. | 535 | 1,466 | 183 |
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost, Icemaker (Overall) | 563 | 1,542 | 193 |
| 9 to 14 cubic ft. | 475 | 1,302 | 163 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 528 | 1,446 | 181 |
| 20 to 24.9 cubic ft. | 583 | 1,598 | 200 |
| 25 to 30 cubic ft. | 612 | 1,676 | 210 |
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost, Through Door Ice Dispenser (Overall) | 670 | 1,835 | 229 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 621 | 1,701 | 213 |
| 20 to 24.9 cubic ft. | 673 | 1,844 | 230 |
| 25 to 30 cubic ft. | 692 | 1,897 | 237 |
| Built-In, With: Automatic Defrost, Without: Icemaker (Overall) | 382 | 1,047 | 131 |
| 9 to 14 cubic ft. | 368 | 1,008 | 126 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 484 | 1,325 | 166 |
| Built-In, With: Automatic Defrost, Icemaker (Overall) | 545 | 1,494 | 187 |
| 9 to 14 cubic ft. | 437 | 1,196 | 150 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 542 | 1,486 | 186 |
| 20 to 24.9 cubic ft. | 604 | 1,654 | 207 |
| Side-by-Side Refrigerator Freezer by Features & Size | Average Annaul Energy Use (kWh/yr) | Average Watt Hours Used / Day (Wh/day) | Average Watts Used / Hour (W/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost, Icemaker | |||
| 25 to 29.5 cubic ft. | 653 | 1789 | 75 |
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost, Through Door Ice Dispenser (Overall) | 618 | 1694 | 81 |
| 19.3 to 24.9 cubic ft. | 598 | 1639 | 81 |
| 25 to 29.5 cubic ft. | 659 | 1805 | 71 |
| Buit-In, With: Automaic Defrost, Icemaker | |||
| 25 to 29.5 cubic ft. | 711 | 1947 | 75 |
| Buit-In, With: Automaic Defrost, Through Door Ice Dispener | |||
| 25 to 29.5 cubic ft. | 776 | 2127 | 89 |
| Refrigerator w/ Top Freezer by Features & Size | Average Annual Energy Use (kWh/yr) | Average Watt Hours Used / Day (Wh/day) | Average Watts Used / Hour (W/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost (Overall) | 342 | 938 | 39 |
| 9 to 14 cubic ft. | 300 | 821 | 34 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 354 | 969 | 40 |
| 20 to 24 cubic ft. | 394 | 1080 | 45 |
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost, Icemaker (Overall) | 452 | 1237 | 52 |
| 9 to 14 cubic ft. | 404 | 1108 | 46 |
| 14 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 445 | 1220 | 51 |
| 20 to 24 cubic ft. | 477 | 1307 | 54 |
| Single Door Refrigerator w/o Freezer by Features & Size | Average Annual Energy Use (kWh/yr) | Average Watt Hours Used / Day (Wh/day) | Average Watts Used / Hour (W/h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Standing, With: Manual Defrost | |||
| 20 to 23.8 cubic ft. | 331 | 907 | 38 |
| Free Standing, With: Automatic Defrost (Overall) | 335 | 916 | 38 |
| 16 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 303 | 830 | 35 |
| 20 to 23.8 cubic ft. | 338 | 927 | 39 |
| Built-In, With: Automatic Defrost (Overall) | 280 | 767 | 32 |
| 7.6 to 11.9 cubic ft. | 248 | 680 | 28 |
| 12 to 15.9 cubic ft. | 272 | 745 | 31 |
| 16 to 19.9 cubic ft. | 301 | 824 | 34 |
Frequently Asked Questions
-
How much does the electricity cost to run a refrigerator?
The average refrigerator uses 1,429 watts per day, which when converted to kilowatts, equals 1.429 kW per day. The national average cost of a kilowatt is 15 ¢/kW. Multiplying kW/day times ¢/kW equals electricity cost. (1,429 watts x 0.15 cents = 0.21 cents per day)
-
Can you run a refrigerator on a solar generator?
Yes, you can power a refrigerator with a solar generator. Just be sure to choose one that can provide enough AC current to start and run your fridge. There are many on the market with solar inverters that cannot provide the starting watts needed. Choose wisely.
-
How many watts does a refrigerator use in 24 hours?
The average refrigerator uses 1,429 watts in 24 hours. Which works out to 60 watts per hour on average.
Wrap Up
Knowing your refrigerator’s power consumption is vital if you need to power it with a portable power station or generator.
Refrigerators without a freezer use around 804 watts per day, while those with freezers consume around 1,429 watts daily.
You’ll also need to consider the starting watts needed to initiate the refrigerator’s operation, which can range from 350 to 1,200 watts.
Before purchasing a power solution, consider checking the appliance’s ENERGY STAR® rating and use an electricity usage meter for more precise measurements. Understanding these details will enable you to make an informed, energy-efficient decision.
